Seeing no future in the Carolinas and unwilling to vegetate at Wilmington, Cornwallis marched north into Virginia, where he joined forces with troops under Benedict Arnold. (Disaffected by what he considered unjust criticism of his generalship, Arnold had sold out to the British in 1780. He intended to betray the bastion of West Point on the Hudson River. The scheme was foiled when incriminating
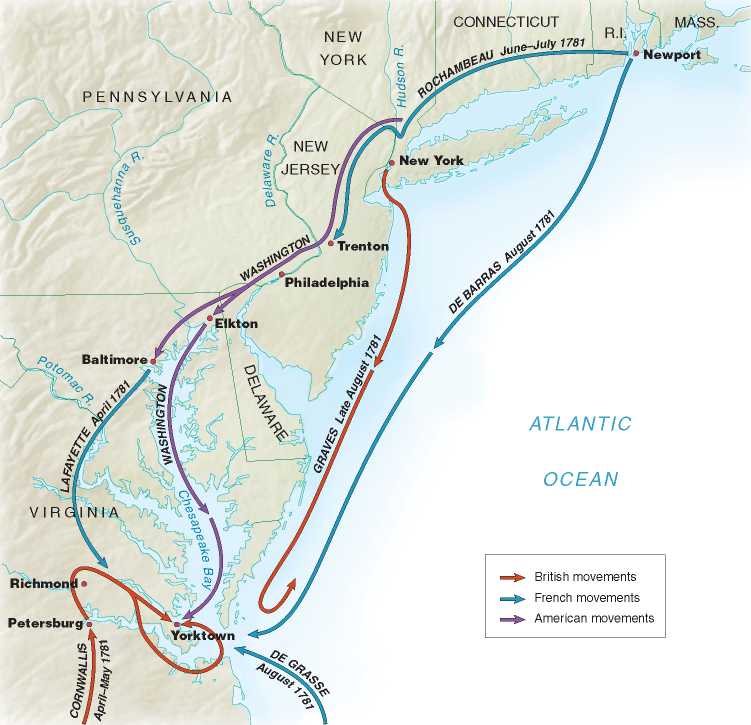
The Yorktown Campaign, April to September 1781 Cornwallis assumed that his army at Yorktown could be provisioned and, if necessary, evacuated by the mighty British navy. But when several French admirals converged on the Chesapeake Bay in August and defeated the British fleet commanded by Admiral Graves, Cornwallis was trapped. He surrendered in October.
To attack the British base at New York, but at the urging of Rochambeau he agreed instead to strike at Yorktown. After tricking Clinton into thinking he was heading for New York, he pushed boldly south. In early September he reached Yorktown and joined up with an army commanded by Lafayette and troops from de Grasse’s fleet. He soon had nearly 17,000 French and American veterans in position.
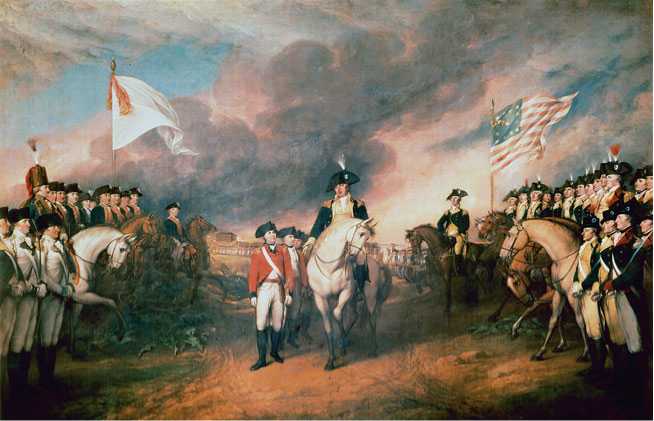

This painting of the surrender of Cornwallis at Yorktown on October 19, 1781 was done by John Trumbull in 1820. Trumbull's original version of the painting depicted Cornwallis in the act of surrender. But this was a serious mistake: Cornwallis, unwilling to admit defeat in person, had sent a subordinate to surrender on his behalf. Trumbull repainted the scene, changing the uniform color of the central figure from red to blue: An American officer reaches for a sword presented by Cornwallis's second-in-command.
Cornwallis was helpless. He held out until October 17 and then asked for terms. Two days later more than 7,000 British soldiers marched out of their lines and laid down their arms. Then the jubilant Lafayette ordered his military band to play “Yankee Doodle.”
((!•—[hear the Audio The Liberty Song at myhistorylab. com
Papers were found on the person of a British spy, Major John Andre. Arnold fled to the British and Andre was hanged.) As in the Carolina campaign, the British had numerical superiority at first but lost it rapidly when local militia and Continental forces concentrated against them. Cornwallis soon discovered that Virginia Tories were of little help in such a situation. “When a Storm threatens, our friends disappear,” he grumbled.
General Clinton ordered Cornwallis to establish a base at Yorktown where he could be supplied by sea. It was a terrible mistake. The British navy in American waters far outnumbered American and French vessels, but the Atlantic is wide, and in those days communication was slow. The French had a fleet in the West Indies under Admiral Francois de Grasse and another squadron at Newport, Rhode Island, where a French army was stationed. In the summer of 1781 Washington, de Grasse, and the Comte de Rochambeau, commander of French land forces, designed and carried out with an efficiency unparalleled in eighteenth-century warfare a complex plan to bottle up Cornwallis.
The British navy in the West Indies and at New York might have forestalled this scheme had it moved promptly and in force. But Admiral Sir George Rodney sent only part of his Indies fleet. As a result, de Grasse, after a battle with a British fleet commanded by Admiral Thomas Graves, won control of the Chesapeake and cut Cornwallis off from the sea.

 World History
World History









